How To Search The Internet Properly
Learning how to search the Internet properly is a basic but key skill I think everyone should have. Search Engines are our portal in to the Internet, and understanding how they work, and how to use them, is the key to efficiently getting the most out of them.
This article looks at how to search the Internet by focusing on how search engines work. We then look at how to use the world's most popular, search engine, Google. This includes some of Google's advanced search options.
Once you understand the mechanics of Internet searching and how Google works, we look at some tips and tricks for undertaking time-saving search activities. This includes something called boolean and wildcard searching. Don't worry, though. It is easier than it sounds.
We also touch on some child safe Internet search engines designed to protect our children from more unpleasant results.
Join The Human Byte — Get The Ultimate BIOS Update Guide
- Receive the Ultimate BIOS Update Pack
- Includes a set of checklists, flowcharts, and your Beep Code Finder support your BIOS update process
- Also includes a full set of eBooks including a Survival Guide and step-by-step Support Guide
- Receive regular emails with practical information you can use
- I only use your e-mail for the newsletter. Unsubscribe anytime.

How Internet Search Engines Work
Search engines are not required if you know the web address, or Uniform Resource Locator (URL) of the website you intend to visit.
However, what if you do not know the web address, or do not have a particular website in mind?
This is where search engines comes in, and your knowledge on how to search the Internet becomes useful.
Think about search engines as holders of a large index of all the web pages and their content that the engine is aware of, or has discovered to date. This is similar to the index of a textbook that contains words and phrases.
When you enter the words you want to search, the engine rapidly returns from its index all the links to web pages that relate to your query. It is then up to you to sort through the returns to find the information you need.
This is why it is useful to think about the words you put into your search query. If you use too many words, you may get a limited number of results, or returns. If you don't use enough words, the web link returns could run in to the multi-millions.
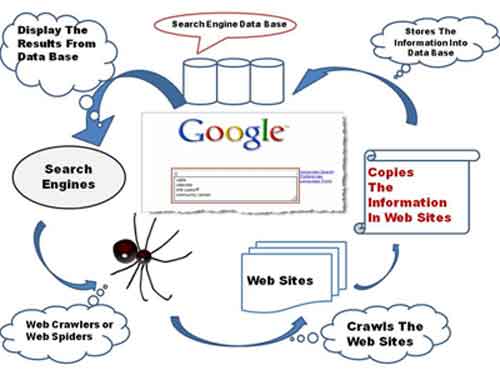 How To Search The Internet
How To Search The InternetHow Search Engines Work
Source:- tinobusiness.com
The index is maintained by a program called a web crawler, which is also known as a spider or spider bot. This program automatically browses new and updated web pages, takes a copy of the index, and includes relevant information to help with your search.
The web crawler then checks all other pages that are linked to the one in question, repeating the actions of copying pages and indexing information.
Search engines are incredibly complex. Their vast number of algorithms are built to try to make sure the most relevant and highest quality web pages are returned first. However, this is a work in progress for all search engines.
For example, the PageRank algorithm evaluates the popularity of a particular web page. The more links there are to that page, the higher the perceived quality of that page, and is therefore a contributory factor in where the page appears when its associated keywords are retrieved.
The short video below is a more comprehensive overview of how search engines work. It is brilliantly explained in simple to understand language.
The Internet | How Search Works Video
Using Google | An Overview
Google is the most popular search engine in the world. There are other engines available, but Google tends to be the one most people use daily.
Most people simply open Google, enter their words and click the Google Search button or hit the return key. They then look at the first page or two, and if the returns are not satisfactory, they enter a slightly different word or phrase, and review the next set of results the engine returns.
However, Google includes some additional features, that you may not be aware of, that can help with your endeavours. We have a look at some of these features below.
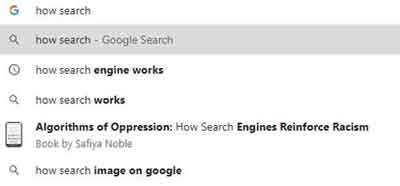 How To Search The Internet
How To Search The InternetAn Example of Google Instant or Autocomplete in Action
The Google autocomplete feature is actually a search prediction technique that completes word phrases when entering your criteria. You can see in my example above how it can also include references to books, and indeed other forms of media.
Autocomplete delivers mere suggestions for criteria that the search engine 'thinks' you could be interested in. This is based on many factors, such as popularity or similarity.
This feature can be disabled if required. I leave it switched on. It has proven useful at times when searching for new content to write about, for example.
Once you complete entering your search, the first results page appears. Have a look at the image below for how Google can organize the results that you see.
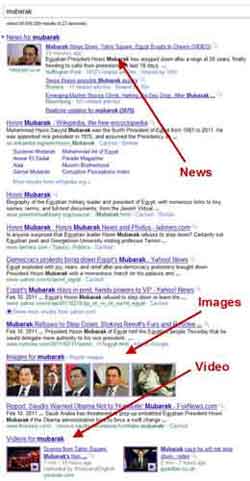 How To Search The Internet
How To Search The InternetGoogle Search Results Example
Source:- searchengineland.com
For popular search words or phrases, Google's first page can often be a mix of news articles, images, videos, adverts, and even a description of a company, like Apple for example. When searching for instructions such as how to install a sound card, Google will typically display a snippet of the instructions from the top web page returned.
Furthermore, if looking for a definition of a specific word, maths calculations or translating language, Google will typically present the answers or responses at the top of the results page.
Across the top of the result's page is further information, such as how many results were returned, and in what time, which is usually less than half a second.
Note the different categories or tabs such as Videos, Images, and News. Simply click on the category link at anytime to focus your search in the given category areas. I find the image tab very useful. A picture paints a thousand words in the Technology sector.
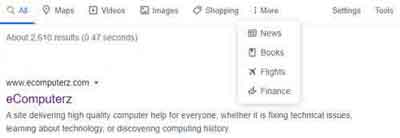 How To Search The Internet
How To Search The InternetGoogle Search Categories or Tabs
Google also has Settings and Tools options. The Tools option simply enables you to focus your search in 'indexed pages' from a given period, such as the past 24 hours or past year. This can be a useful feature when looking for the latest but specific news articles.
There is also an option to focus your results on your criteria verbatim. This means the search results are based on your words in the same order in which you typed them in.
The Settings option includes further refinement to your search criteria, such as setting your safe search filters and the number of links presented on each page of your results. See the Search Settings option for more detail.
You also have the option to perform your search in different languages, and the Advanced Search option enables you to define how your criteria is processed. For example, by word exclusion, or verbatim as mentioned earlier. To review your Internet Search History, have a look at the Search Activity option.
The Google search engine also enables you to speak your words or phrases. This can be very useful if your hand dexterity is limited. You do need a microphone, which most modern devices have included.
Take a moment to investigate each option and have a play with the settings to see what works best for you.
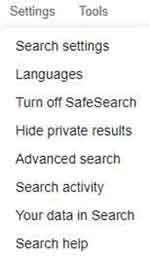 Google Settings and Tools
Google Settings and ToolsBelow is a fantastically simple three-step guide on how to search the Internet properly. An important observation here is to acknowledge the fact the more search engines exist besides Google.
The next most used Internet search engines today are Bing (From Microsoft) and then Yahoo. Although they do lag somewhat behind Google. There are also search engines, such as DuckDuckGo, that promise not to track or hold your data. If privacy is significant to you, then search engines such as this are worth considering.
 How To Search The Internet
How To Search The InternetEffective Search Tips
Source:- simonhaughton.typepad.com
Tips And Tricks For Smarter Searching
This section runs through some tips and tricks to focus your search activity and hopefully make the whole experience much better and efficient.
In the first section of this article, we looked at how Internet Search Engines worked. I think it is fair to say that Google, and indeed other search engine providers, have the computing aspect of search well understood.
However, what still needs to evolve in the world of search is the human aspect? Artificial Intelligence could be the answer one day. However, the following tips and tricks should support your smarter searching when using Google.
Use Quotes
Quotation marks refine the search to that specific phrase, in the order in which you typed it in. This is one of the best tricks to limit the number of web pages returned in your results.
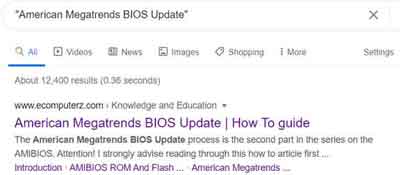 Internet Searching Tips and Tricks
Internet Searching Tips and TricksQuotation Marks Example
Use a Hyphen or Minus Sign
This tip is brilliant for focusing your search where there are potentially two or more ambiguous meanings. For those up to speed with their algebra, this is one of the boolean searches on the Internet with a NOT operator.
For example, if you want to look for new windows, but don't want anything to do with the Microsoft Windows Operating System to cloud your results, simply enter: “Windows -Microsoft”.
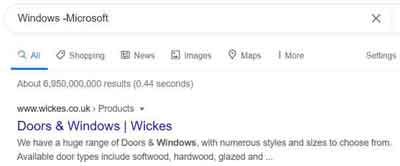 Internet Searching Tips and Tricks
Internet Searching Tips and TricksMinus Operator Example
Use A Colon
The colon is used to focus your search to a specific website, and to find sites that are similar, or related to the one you are interested in. The Syntax is straightforward to use.
For example, to find sites related to Microsoft, simply enter related:www.microsoft.com.
A more obscure use of the colon in Google searches is the link option. This looks for sites that have linked the specific website of interest. For example, to find sites that linked to eComputerZ, simply enter link:ecomputerz.com.
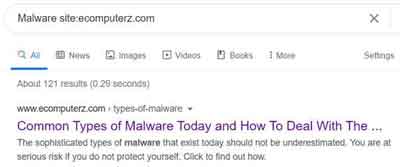 Tips and Tricks
Tips and TricksSite Colon Example
Use The Wildcard Internet Search Syntax
A wildcard Internet search, or asterisk searches, are incredibly useful. This is also known as the fill in the blank operator. It leaves a placeholder for the search engine to complete as it 'sees appropriate'.
For example, if you have heard of American Megatrends but don't know it is a BIOS vendor, you could simply enter “American Megatrends* Update” and Google will complete the missing word or phrase. This trick is also very useful for finding out song lyrics when you only know a few works in a chorus.
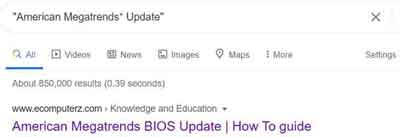 How To Search The Internet Tips and Tricks
How To Search The Internet Tips and TricksWildcard Example
Attention!
You cannot use wildcard searches to complete parts of words. For example, “American Mega* Update” will not work.
Use the OR Operator
Using OR is a technique to search for multiple phrases. This type of search flexibility can help you to narrow down your results and increase the chances of Google returning the exact results you want.
The example in the image below is requesting Google search for Types of Malware and information on a specific Malware type called Wannacry.
The Pipe | symbol can also be use in your search entry, and Google will interpret this as the OR operator.
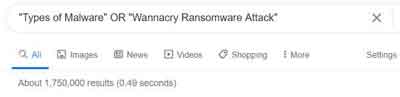 How To Search The Internet Tips and Tricks
How To Search The Internet Tips and TricksThe OR or | (Pipe) Operator Example
Attention!
The 'opposite' operator OR is AND. You can also use the Plus Symbol (+) in your search criteria. For example, BIOS AND UEFI, or BIOS + UEFI, returns results that contain both words.
Other Search Tips and Tricks
Google has dozens of search techniques available to refine your criteria. I've put a link in the final thoughts section of a fantastic source that explains most, if not all, the techniques available today.
To round off this section, here are a few more tips and tricks to try out:-
- Define — The inbuilt Google dictionary, e.g. define:artificial intelligence
- File Type — For document types, e.g. malware filetype:pdf
- Intitle — For searching web page titles, e.g. initile:how to search the internet
- Weather — For weather forecasts e.g. weather:uk
- Conversions — For converting currency or units, e.g 1 mile in km
How to search the Internet beyond the basics is to think about combining some search options together. In the OR operator example above, I combined the OR Operator and Quotation Marks together.
How to Search The Internet | Final Thoughts
With some practice, learning how to search the Internet properly will give you a more efficient approach to Internet searches and improved targeted results that are more likely to be in line with your thinking.
However, the Internet does not necessarily have every answer to everything yet. Therefore, try not to spend your life looking for something you potentially cannot find because it simply does not exist. Give yourself a time limit and move on is my advice.
Our children are more technically savvy than ever, and they likely know how to search the Internet. However, as we know, the Internet has a dark side, and some search results can have unintended consequences of what they could potentially return to your child's screen.
With that in mind, it is worth noting that there are child safe internet search engines available, such as Kiddle.
AHREFS is a comprehensive reference page for dozens of Google Advanced Search Operators. Have a look and enhance your knowledge.
