What is Fibre Broadband? A Basic Guide For Everyday Online Users
What is fibre broadband? It is a question I often see in forums and on websites. However, I usually feel unsatisfied at the answers. This is because they are either too vague, or are on a commercial broadband provider's website that is geared up to sell you their product.
This article is my take on answering the question. We have a look at how fibre broadband works, and review the benefits and disadvantages that fibre connectivity offers home users.
The sister article to this page explains how to set up your home fibre broadband like a professional. I recommend reading this article first, then reviewing the home broadband setup article to ensure you have the best wireless coverage and secure connection possible,
Join The Human Byte — Get The Ultimate BIOS Update Guide
- Receive the Ultimate BIOS Update Pack
- Includes a set of checklists, flowcharts, and your Beep Code Finder support your BIOS update process
- Also includes a full set of eBooks including a Survival Guide and step-by-step Support Guide
- Receive regular emails with practical information you can use
- I only use your e-mail for the newsletter. Unsubscribe anytime.

What Is Fibre Broadband, And How Does It Work?
I think to understand what fibre broadband is, we need to first explore how it works. Back in the 1990s, “Dial-Up” modems connected us to the Internet at chronically slow speeds compared to today's standards.
I recall using the 56 Kbit/s models and implementing the 33.6 Kbit/s models in GP Practices in my early technician days. The cost if I recall was something like £14.99 per month.
Modem's used your telephone line, and dialled in to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for Internet access.
When you manually connected to your ISP, anyone who tried to call your home would be greeted by an engaged tone. Internet connectivity in those days consumed your telephone line just like a phone call would.
 What Is Fibre Broadband?
What Is Fibre Broadband?The U.S Robotics 56k Modem
By the early 2000s, Broadband was launched, and by 2005, we were connecting to the Internet at 2 Mbps. This was phenomenal speed compared to modem's, and it opened up a new world of possibilities, such as video and music, which was simply not possible throughout the modem period.
Early broadband was based on “Asymmetric, Digital Subscriber Line” technology, or ADSL for short.
This technology connected us to the Internet by using the same copper-based telephone wires to our homes as modems. The difference is ADSL uses a different frequency as traditional voice-based services modem's, and our traditional phone calls, use.
This means, with the use of “Digital Subscriber Line”, or DSL filters (also known as splitters), plugged in to our telephone sockets, and a Broadband Router, we could make and receive telephone calls, and connect to the Internet at the same time. This is the technology we are familiar with today.
The “Asymmetric” part simply means faster download speeds than upload speeds. The service is “Always On”, meaning you don't have to manually “Dial” your ISP to connect to the Internet, like in the modem days.
I recall my first broadband service cost £24.99 per month, and there were much more expensive ISP services on the market at the time.
 What is Fibre Broadband?
What is Fibre Broadband?A Fibre Broadband Filter
“Standard Broadband” was superseded by Fibre Broadband from around 2008. I subscribed to my first Fibre Broadband service in 2011, and it improved by connection speed from 1.5 Mbps to 4 Mbps.
It is worth mentioning at this point that the closer your home is to the Telephone Exchange, the faster your Internet connection is. There are many technical reasons for this that are beyond a basic computer section article!
The demands for faster Internet speeds, and I suspect a reduction in the costs of fibre cabling, ushered in the era of Fibre Optic Broadband services.
This is also known as “Fibre To the Cabinet” or FTTC. Fibre cabling uses light to send and receive data. This means it is incredibly fast.
Service providers replaced the copper cabling between the Telephone Exchange and the “Street Cabinet” near your home. There is a lot less work (and cost) implementing fibre between Street Cabinets and Telephone Exchanges, than Street Cabinets and all the individual homes.
Below is a picture of a typical Street Cabinet you would see all over the United Kingdom.
 What is Fibre Broadband?
What is Fibre Broadband?A UK Street Cabinet or "Green Man"
Source:- increasebroadbandspeed.co.uk
The fibre part of the connection between your home and the Telephone Exchange is where the boost in connectivity speed comes from. At the time of writing, my home Internet speed is 40 Mbps. Much faster connectivity exists too.
However, the speed slows down somewhat when the Street Cabinet converts the fibre light signal, to the copper electrical signal your home phone line uses. This is why Internet speed continues to be faster, the closer you live to both the Telephone Exchange, and the Street Cabinet.
The picture below shows the inside of a typical UK Street Cabinet (You've always wondered what they look like inside, haven't you?).
 What is Fibre Broadband?
What is Fibre Broadband?Inside A Typical UK Street Cabinet
Source:- ispreview.co.uk
“Fibre To The Premises”, or FTTP, is where the copper telephone line to your home or Business is replaced with fibre optic cabling.
This means Internet speeds are lightening fast with end-to-end fibre cabling between your home and the Telephone Exchange. However, “Super Fast Broadband” is also expensive, and difficult to install.
Some Internet Service Providers use Coaxial cabling, replacing the traditional copper telephone lines to people's homes. Although this is not as fast as fibre, it is capable of speeds much faster speeds than telephone lines.
The image below illustrates the three connectivity types explained above very well.
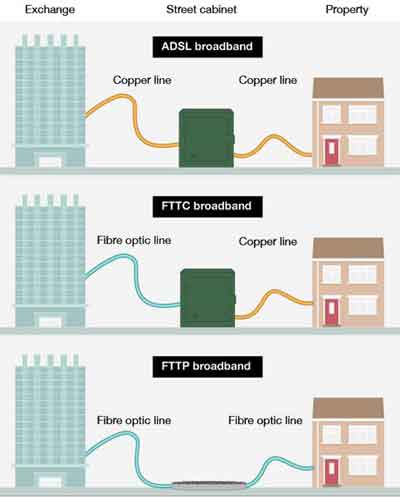 What is Fibre Broadband?
What is Fibre Broadband?Past - Present - Future Connectivity
Source:- bbc.co.uk
What Are Fibre Broadband Advantages?
There are several benefits over standard broadband when you connect to the Internet through a fast broadband service. For example, data transmission via light is an automatic security improvement because the data cannot be “read” in this format.
The big benefit is the positive consequences of the higher connectivity speed. This means you can download content, upload data more quickly and search the Internet faster.
If you are an avid Netflix, Amazon Prime or other streaming media viewer, then a fibre broadband service ensures your stream is seamless, i.e. no video breaks or pauses, or audio synchronization and “Jitter” issues. On-demand TV is more or less instant over fibre when you select your programme, too.
Jitter is a term used to describe small but noticeable delays during data transfer. This can occur when your broadband connection is too slow or congested by too many devices like PC's and Tablet Computers streaming at the same time. For audio this manifests itself as delays, pauses or break up of music or the spoken word, which is frustrating, especially for music lovers.
Broadband congestion affects everyone in your home. I know friends and colleagues who have slower connectivity but also have multiple devices connected to their home wireless router e.g. Smart TV's, Tablet Devices, Laptops, Alexa, Mobile Phones etc.
When one member of the family streams YouTube video's, everyone else's Internet speed plummets, resulting is disconnections, delays, and arguments.
Therefore, to avoid these issues, invest is fibre broadband. You are provided with a wireless router for fibre broadband connectivity when you sign up with your ISP. This is a benefit because it enables all family members to connect from wherever they are in your home.
 What is Fibre Broadband?
What is Fibre Broadband?A Typical Home Broadband Fibre Wireless Router
Source:- choose.co.uk
A fibre connection is also usually more stable and consistent in delivering Internet speeds than previous connectivity services. In the early days of standard broadband, there would be noticeable external congestion issues at peak times and weekends. Today, this is rarely an issue.
Another benefit of this consistent “bandwidth” is a more seamless experience when working from home. During the COVID-19 Pandemic, home working figures increased beyond most peoples expectations. There was a lot of work in a short space of time by Organizations increasing their VPN, or Virtual Private Network, connectivity capacity.
Alongside home working was the proliferation of desk-based video conferencing using services such as Microsoft Teams and Zoom. Those without a good fibre broadband connection experienced frequent dropouts and had to reconnect to their Organization's VPN service, sometimes losing work and missing vital parts of their conferencing sessions.
With every benefit, there is a drawback. To present a balanced view, the next section looks at disadvantages of fibre broadband.
The Disadvantages of Fibre Broadband
As a service, fibre broadband has very few disadvantages apart from cost. The faster your connection requirements, the higher the cost.
However, the fibre cabling itself is a different story. It is quite fragile compared to traditional copper cabling because of the cable's glass element.
This means it is subject to accidental damage, especially if there is construction going on near the cable routes, and is subject to breakages when being installed underground.
 What is Fibre Broadband?
What is Fibre Broadband?Damaged Underground Fibre Cabling
Source:- norscan.com
Some fibre components are subject to corrosion through water damage, and rodents getting into the ducts and chewing through the fragile cabling.
I've also read stories about fibre being damaged by lightening storms. Lightening searches for the best available conductor when it strikes the ground. This includes any underground cabling. If it chooses the protective casing of the fibre cabling, then damage to the fibre cable itself is more than likely.
Thankfully, the disadvantages of fibre cabling are not a frequent occurrence. Most ISP's have what they call physically diverse cable routes in place. This simply means if one fibre cable gets damaged, your service can still be provided via the other fibre cables that are not damaged.
What is Fibre Broadband | Final Thoughts
Fibre broadband is fast becoming the standard method of connecting to the Internet in our homes. It provides quick and efficient connectivity that enables us to take for granted instant streaming TV, gaming, and music without a second thought. This is how it should be.
My advice is to spend some time finding the best fibre optic broadband service available for your home. If you can afford it, buy it. If you can't afford it, work out your maximum budget and see what is available.
Please note, ISPs are registered with comparison sites and cashback sites, and they usually have special offers for new customers. Don't accept their first offer. Haggle the price down or the service extras up. Furthermore, don't be afraid to change suppliers when your contract ends. The price often increases dramatically if you let your contract lapse.
If you have ever asked yourself the question: What is fibre broadband? I hope this article goes some way to answering your query.
To learn in more detail about fibre broadband, have a look at this article on the Increase Broadband speed site.