Solid State Hard Drive
The Solid State Hard Drive is now a viable alternative to the traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD) for home computer users.
However, there are several factors I think you must consider before deciding whether this type of hard drive is appropriate for you at this time.
This article explains what a Solid State Hard Drive (SSD) is and how it differs from traditional Hard Drives. It also poses various scenarios to help you decide whether this type of HDD is right for you.
Join The Human Byte — Get The Ultimate BIOS Update Guide
- Receive the Ultimate BIOS Update Pack
- Includes a set of checklists, flowcharts, and your Beep Code Finder support your BIOS update process
- Also includes a full set of eBooks including a Survival Guide and step-by-step Support Guide
- Receive regular emails with practical information you can use
- I only use your e-mail for the newsletter. Unsubscribe anytime.

What Is A Solid State Hard Drive?
A Solid State Hard Drive does not look much different from a traditional Hard Drive for a desktop computer or laptop.
They both do the same job of storing your data and the files that run your Operating System and programs.
However, the technology that underpins them vastly differs, and therefore so do things like durability, performance, capacity, and cost.
 Solid State Hard Drive
Solid State Hard DriveThe aesthetic similarities between the SSD (Left) and the traditional HDD (Right)
Available for some time now, SSD technology was traditionally expensive and usually found in large data centre servers only.
More recently, as costs decrease, Solid-State Drives (or Flash Memory) have come into the home computer mainstream through Tablet technology such as the Apple iPad.
In tablet devices, the inbuilt flash memory is embedded on the motherboard. In PC's and Laptops, SSD's ultimately plug into the motherboard just like traditional hard drives.
A Solid State Hard Drive is made up of RAM boards (Random Access Memory) rather than a traditional rotating disk platters.
Like an old vinyl record the head, or needle, reads (and writes) your information to and from the tracks on the disk platter (you can't see these tracks, but they are there, storing your magnetized data).
Like an old record player, the vinyl record (i.e. disk platter) must be spinning at the right speed for the data to be accessible. The image below illustrates the technical differences.
 The Internal Difference Between a Solid-State Drive
The Internal Difference Between a Solid-State Driveand Traditional Hard Disk Drive
Traditional RAM is volatile. This just means that the information stored on it, e.g. your loaded programs and files, are not retained if your machine loses power.
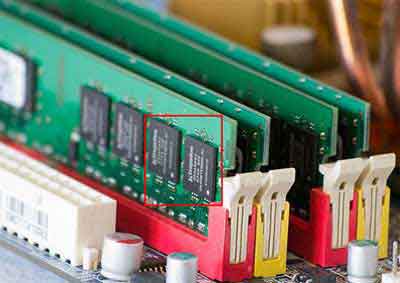 Traditional PC RAM Sticks
(RAM Boards Highlighted)
Traditional PC RAM Sticks
(RAM Boards Highlighted)SSD RAM is non-volatile. This just means that information stored in it is not lost when your machine loses power, i.e. just like a traditional hard drive.
Why Should I Consider A Solid State Drive?
Other articles on the Internet usually say something like, “Solid State Hard Drives are reportedly more durable and better performers than traditional Hard Drives. However, they also hold less capacity and are more costly”.
What does that last paragraph actually mean? In this section, we dissect this paragraph and look at each element in more detail.
Durability
The fundamental differences in the technologies mean Solid-State Drives are more durable. This because more things can go wrong with a traditional hard drive due to the moving parts within them, including:-
- Motor/spindle issues, i.e. what makes the platters spin and therefore your data readable;
- Drive Arm failures and Drive Head Crashes, including scratches on the platters, which means your data and programs cannot load and potentially your data lost forever;
- Jarring or jolting the hard drive, especially when in use, e.g. dropping your Laptop, can cause non-recoverable mechanical failures;
- Other things such as dust can impact the way the mechanics of the traditional hard drive work.
These issues with traditional drives are not possible with the solid state versions. As there are no moving parts, the power required to run a Solid State Hard Drive is much less than a traditional hard disk. This makes them very attractive for inclusion in Laptops and other portable devices.
Performance
The performance of a SSD is much better than a Hard Drive. There is a notable improvement in the time it takes to load the Operating System, Programs, and Files.
For Microsoft Windows using Sleep or Hibernation settings, recovery time is much quicker. Installing software and game play is also enhanced.
Some SSDs include encryption, which means your data is protected if your machine is stolen or misplaced.
The image below highlights the differences between traditional hard drives and solid-state drives.
 A typical comparison of traditional hard drives and solid-state drives
A typical comparison of traditional hard drives and solid-state drivesSource:- gamingscan.com
The difference in performance is because of the way the RAM boards work on Solid-State Drives.
The bigger the drive, the better the performance too. The reason for this is very technical, but basically the more 'NAND chips' (RAM boards) your SSD has, the better the performance.
SSD's also come with an inbuilt processor. Combined with RAM boards, they can produce high Input/Output (I/O) rates through sequential Read/Write capabilities.
This just means solid state hard drives can read and write information at the same time, but incredibly quickly.
Input/Output refers to the data that transfers to or from your computer or peripherals, such as a printer, for example.
Traditional hard drives can only read or write data (but not both at the same time). Latency (or delay to the normal speaking world) in inherent because Read/Write activity can only happen when:-
- The platters spin up to the maximum speed (Limited by RPM);
- The arm and head move to the right position on the track to read or write the data you are dealing with.
Combined, the traditional hard disks I/O rate is much lower, making them slower than solid-state drives.
All hard drives, including solid state ones, slow down over time, and stop working too. Wear and Tear sees to this!
With traditional HDD's, you can improve performance by carrying out tasks such as defragmenting your drive, using utilities such as Defraggler.
For Mac OSX users, software such a Trim Enabler cleans up your solid-state drive and reports improving performance and extend the life of your drive.
It is worth noting at this point that SSD's still have a limited lifespan compared to traditional HDD's.
Due to how the technology works, your SSD can only manage a fixed number of write commands. This just means the number of times you click the Save button.
However, don't worry, for the average home computer user, this means your SSD will serve you exceeding 5 years before the RAM boards become unstable through wear and tear.
In this time, there is a high chance you will have already replaced your device with a new one anyway.
Capacity and Cost
Capacity is the size, in Gigabytes (GB) these days, of your hard drive. It determines how much you can install or save.
Storage capacity was limited, but is quickly gaining parity with traditional drives. Typically, 256 GB SSDs are provided with modern laptops.
However, there are SSDs's with 1 TB (Terabyte) capacity on the market.
There are some SSDs that are up to 1 TB in size, and even some that are up to 6 TB in size. The Samsung 860 EVO 1 TB SATA 2.5 Inch Internal SSD, for example, is suitable for both PCs and Laptops.
In terms of cost, SSDs are still pricier. However, this cost is constantly falling, which means they are now a valid alternative for home computer users.
Final Thoughts
Is the Solid State Hard Drive right for you? This is a question only you can answer. Consider how you and your family use your computer or laptop. What is more important, performance or capacity?
If you are a gamer, impatient or generally like things to be done quickly, and you do not store much data, then a solid state hard drive is a serious option for you, assuming you agree with the cost.
If you are not too concerned about speed, but are into digital photography, making videos and other multimedia tasks, a traditional hard drive is for you.
Consider whether you really need a large amount of local storage space, especially with cloud services available.
If you are undecided, there are alternative options available to you, including:
- Put a SSD and HDD into your machine. The SSD could run your Operating System and programs, and your larger HDD could store your data. The HDD could be external (USB connected)
- Consider a Hybrid Drive, providing the best of both worlds in a single hard drive
If you decide to change your hard drive, and your machine is relatively new, check with your supplier to ensure you do not invalidate the warranty agreement.
Finally, here is a comprehensive review of the differences between SSD's and traditional hard drives from PC Mag. Worth a read!