What Is CPU Speed And Its Importance To Your Computer's Performance
The CPU speed is still an important factor when buying new computing devices. The pace of modern technology is increasing, with fast internet access, software evolution, and the demand for instant responses to our requests.
We need faster computers to handle the faster technologies they connect to, including quicker wireless access. Therefore, we require computer processors that can handle the challenge.
To understand and appreciate what constitutes the CPU processor speed, this article discusses what the CPU is, how it works, and the factors that make up processor speed. We also look at why this matters to your computer's performance.
Join The Human Byte — Get The Ultimate BIOS Update Guide
- Receive the Ultimate BIOS Update Pack
- Includes a set of checklists, flowcharts, and your Beep Code Finder support your BIOS update process
- Also includes a full set of eBooks including a Survival Guide and step-by-step Support Guide
- Receive regular emails with practical information you can use
- I only use your e-mail for the newsletter. Unsubscribe anytime.

What Is A Central Processing Unit?
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is considered the brain of your computer. Every device we use has one, and, it is critical to everything computing devices do.
It is a piece of hardware that is plugged in to your device's motherboard, and come in different shapes, sizes, and features.
Modern processors are designed on silicon semiconductor chips, and contain millions of transistors, or electrical switches, which are used to process data.
The image below shows a typical CPU, with the transistors displayed on the left. These usually plug into the CPU socket on the motherboard, so matching the processor spec to the motherboard is critical, especially when building a computer yourself, or replacing the processor.
 CPU Speed
CPU SpeedA Typical Modern Computer Processor
Source:- ecomputertips.com
The processor enables all the interactions we take for granted, such as the applications we use that are either cloud hosted, or locally installed on our device.
The purpose of a CPU is to process data, and execute the input commands we undertake, such as opening e-mails, saving changes to files, and online browsing.
However, the efficiency at which such commands are processed, depends on your CPU speed, and this is determined by many factors, but in particular, the processor core and the CPU cache.
To understand the processor core and cache, it is worth first describing the components that make up a typical processor.
How Does A Central Processing Unit Work?
A CPU design consists of three main components, These are the Control Unit, the Immediate Access Store, and the Arithmetic/Logic Unit.
The control unit basically manages the data input and output communications between the different hardware components within, and attached to, the device, such as the RAM, HDD and the Display Screen.
The control unit ensures that the signals between the components are delivered correctly and accurately.
The Immediate Access Store is the registers of the CPU. This is where the data of the programs you are using is hosted, whilst the calculations are processed to execute, for example, the commands you are inputting, such as keyboard strokes, and even changing the screen resolution.
Modern devices use Direct Memory Access, which is a feature that enables hardware components to communicate, without involving the CPU. This reduces the load on the CPU and makes modern devices more efficient.
The arithmetic/logic unit (ALU) undertakes the calculations needed to process the data.
There are two calculation methods; the arithmetic method, which is the numeric operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
The second method is the logical calculations such as greater than, and less than comparisons, e.g. 2 < 1.
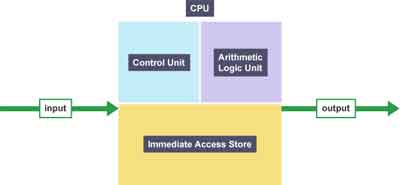 CPU Speed
CPU SpeedCPU Data Flow Diagram
Source:- bbc.co.uk
With an understanding of the CPU anatomy, we are now in a position to look at the factors that comprise the CPU speed, and its ability to carry out its instructions.
Central Processing Unit Clock Speeds
The speed at which your Central Processing Unit can execute instructions is dependent on three factors. These are the processor cores, cache, and the clock speed.
The CPU clock speed uses the computer's internal clock This clock emits a consistent pulse rate, which is used to control and synchronize CPU's activity. Each individual CPU instruction is processed with each passing pulse or tick of the internal clock.
The clock speed is measured in Hertz (Hz), and each Hertz is measured in cycles per second. Therefore, each Hertz is measured by one clock cycle. The faster the CPU speed, in Hertz, the more instructions can be undertaken per cycle.
A CPU with a clock speed of 3 Gigahertz (GHz) can process 3 billion instructions per clock cycle, per second. So, a factor in determining CPU speed is the GHz figure. The higher it is, the faster device instructions are executed.
The fastest CPU clock speed, or frequency, is around 4GHz today.
Early Central Processing Units come with a single core, and very low clock speeds. However, modern processor come with multiple cores. This is like having several CPUs on a single microprocessor chip.
Dual-core (2) and quad-core (4) processors are common today. Quad-core processors, for example, can process 4 instructions per clock cycle at the same time it takes a traditional single core processor to execute one instruction.
An example of a quad-core processor is shown in the image below. Each of the red squares within the black outlines depicts one processor core.
 CPU Speed
CPU SpeedQuad Core Processor
Source:- techradar.com
The more features, such as multiple cores, a CPU has, the more expensive it is to purchase. They also consume more power, although steps are being taken to minimize this as we become more environmentally friendly.
In addition, there is an overhead for the CPU to split instructions requests between each core efficiently, and then merge the different instructions sets after they are processed, for sending to the appropriate hardware component. This can slow the clock speed down slightly.
Finally, the cache is essentially the processor's random access memory. The processor will store in here all the frequent commands and instructions, so they can be processed even faster.
The control unit first checks for the requested instructions in its cache. If the instruction set is not present, the data is requested from the computer's main RAM.
Cache is graded by levels. Level 1 cache is hosted directly on the CPU chip, and is usually the fastest, but smallest, cache. Level 2 and Level 3 caches are typically larger than Level 1, but are slower to access. Occasionally, Level 3 cache is a shared resource across each CPU core.
Cache sizes can vary. Level 1 cache can be up to 2Mb in size. Level 2 and Level 3 cache can be up to 256Mb. I expect these sizes will increase as time passes and technology evolves.
Why CPU Speed Matters To Your Computer's Performance
So, why does all this matter to your computer's performance? As you have seen throughout this article, there are trade-offs depending on the CPU speed, processor core and cache sizes.
Higher clock speeds and fewer cores mean your computer can work with fewer application quickly. However, more cores, and less CPU speed, means your computer can work with multiple applications simultaneously, but at a slightly slower speed.
This is where your personal requirements come in to it. What is your intended use for your device?
For example, if you are a big gamer, then you likely need more CPU cores to handle all the different types of data that needs to be processed, such as the audio and video requirements. Simple Internet browsing and single application access likely needs fewer CPU cores and a higher clock speed.
I think it is always worth maximizing the cache levels whenever possible.
In addition, you still find today that laptops have less CPU power and overall speed than traditional desktop computers. This is because laptops need to conserve power to enhance their mobility when disconnected from a power source.
Costs and your budget should be a major factor in any decisions you make. Don't overstretch yourself financially. Adjust what you use your device for and when instead. This, I think, will help keeps the costs down.
CPU Speed | Final Thoughts
Computer processing is a large topic. For example, the processor architecture, or design, influences the capabilities and ultimately the CPU performance.
The Complex Instruction Set Computing (CISC) design is usually found in desktops and Laptops, whereas Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) designs are usually found in smartphones and tablets.
The differences in designs mean CISC Processors require heat sinks and fans to keep them cool, whereas RISC CPU's consume much less power, and therefore produce much less heat, and have no need for heat sinks.
Overclocking the CPU is possible to improve CPU speed. However, caution is urged. Factors such as system stability, and CPU temperature changes, can easily cause technical problems if you do not know what you are doing.
To support the information presented in this article, have a look at the processor speed article from HP, particularly the sections comparing the different devices.
I am a fan of seeping things simple, and find the articles explaining complex technical information to schoolchildren an excellent source of material. Therefore, have a look at the BBC's Bite Size series on CPU Speed.
Finally, to benchmark your processor speed, especially if you are considering upgrading the CPU, or your device, have a look at the User Benchmark site and their free software download.