Why Is Your WiFi Not Working? A Definitive Troubleshooting Guide!
So, why is your WiFi not working? It is a common theme across the land and something we have all experienced at one time or another.
The other day we had an unexpected power outage in our village, and my first thought was “No Wi-Fi!”. No second thoughts about the fridge warming up, freezer thawing out, security lights or no chance of using the oven or microwave.
This underlines the importance of wireless technology in our daily lives, and is increasingly on a par with water, gas, and other essential utilities. When our wireless access is unavailable, we notice because of what we take for granted these days. I know I do.
It therefore makes sense to cover the important topic of what to do when you are experiencing wireless access issues. That is the theme of this article.
In my experience, troubleshooting Wi-Fi issues tends to fall in to two main areas; The Wi-Fi service itself, and the wireless devices connecting to that service.
Each area has several troubleshooting techniques for you to review and consider using to fix your wireless network issues. Examples include router reboots, service optimization and automatic network connectivity settings. Read on for more ideas.
Join The Human Byte — Get The Ultimate BIOS Update Guide
- Receive the Ultimate BIOS Update Pack
- Includes a set of checklists, flowcharts, and your Beep Code Finder support your BIOS update process
- Also includes a full set of eBooks including a Survival Guide and step-by-step Support Guide
- Receive regular emails with practical information you can use
- I only use your e-mail for the newsletter. Unsubscribe anytime.

Troubleshooting Your Wi-Fi Service
With your WiFi not working, the first steps tend to be focused on the device or devices that are experiencing the issue. This could be no connectivity at all, to intermittent or slower connectivity.
Here, we focus on troubleshooting your Wi-Fi service, which often is the source of the issue affecting all of your household wireless devices.
Here we look at the quick and easy fix that resolves the majority of Wi-Fi issues, why router positioning is important, and what you can do to set up your wireless router for maximum efficiency.
Rebooting Your Wi-Fi Router Often Fixes Wi-Fi Issues
I have experienced both at home and at work the different triggers that disrupt wireless services. For example, the recent power cut prevented my router from loading correctly when power was resumed.
In addition, and just like the majority of all other home devices and technology, spurious behaviour can occur when devices go too long before a reboot. This includes Wi-Fi routers too. Memory leaks can be a common cause of connectivity and service performance issues.
Internet Service Providers (ISP's) can also experience issues at their end. For example, if you are experiencing intermittent disconnects from your wireless service. This could also down to the carrier, experiencing issues, such as your telephone line provider.
Before rebooting your router, check with your ISP and landline provider's service pages to see if there are any planned or unplanned outages affecting your area or postcode.
To reboot, or restart your router, you have two options, which are a soft restart, or a hard restart.
A soft restart is where you use your router software to perform the reboot. This option does not cut the power supply to the router and is usually the quickest, but not necessarily the most effective, restart method. It simply reloads the router firmware.
 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingRestart Wireless Router (Also Known As A Soft Restart)
If a soft reboot does not resolve your issue, try a hard reboot. This is where you cut power to your router by either switching off at the wall and removing the power cord from your router.
In some cases, there is a power on/off button you can use. Wait for at least 30 seconds before reconnecting the power cord, plugging back in to the wall, and switching back on.
This ensures all power to the device has discharged, and any residual data in the device's memory has been fully removed.
 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingLook For Power Buttons and Sockets to Perform Hard Router Resets
Different routers take different amounts of time to fully restart. In my case, it takes up to 4 minutes before the router becomes fully operational.
Once your router is fully booted, try again with your device to access online services. In the majority of cases, a hard reboot resolves the issue.
It is always prudent to understand your routers icons and illuminations, as these are quick indicators as to the current state of your router.
In my case, the router has illuminations such as Green, which means the hub/router is starting up, Steady Orange, which means the router is fully booted but not connected to the ISP's broadband service yet, and Red, which means there is a fault somewhere.
A Steady Blue Light means the hub/router is fully booted, connected to broadband and is working as expected. Any issues are likely down to individual devices, or coverage problems.
 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingFully Functioning Wireless Router
Wi-Fi Router Positioning is Important
In years gone by, old analogue telephones were plugged in to an RJ11 socket positioned next to a window, or the front door (certainly in the UK).
This practice hasn't really changed over the past years and consequently, many routers are positioned towards the periphery of the home, i.e. near front doors and windows.
This means a lot of the wireless signal is either being blocked by the walls or is distributed towards the next door neighbours, or into your garden or street.
The remaining part of your routers wireless range provide coverage inside your home, but not necessarily covering all of your home, and the signal strength required to run all of your household wireless devices efficiently.
The image below is a good example of what I mean. The red and yellow areas will have good wireless coverage where the router is located.
However, towards the blue areas you would see poor to zero wireless coverage, and with your wireless not working, or working properly in these areas, comes the frustration and limitations on where and how you use your household devices.
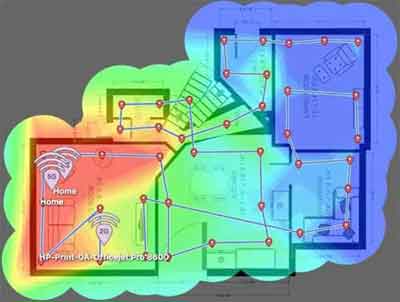 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingExample of A Heatmap Showing Wireless Coverage Quality Inside A Home
Source:- techdigest.tv
The way to resolve this issue is to try to move your router to a more central location. However, I appreciate this is not always possible.
There are techniques you can use to extend your wireless coverage without moving your router from its original position. Have a look at the improving your wireless signal coverage section of the home broadband setup article for ideas. This can be especially helpful when your home has thick walls or lead-lined concrete floors/ceilings, as I have found in my home.
In addition, make sure there are no obstacles in the way of your router, i.e. boxes or other devices. I've seen Wi-Fi routers locked in old, thick cupboards before, and the occupiers wonder why their Internet performance is poor occasionally.
Finally, routers operate at two different frequencies; 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Unfortunately, microwave ovens also encroach on the 2.4GHz range.
If you find wireless connectivity is sporadically intermittent, check to see if the loss of connection correlates with using the microwave ovens in your home. DECT phones (Digital Enhanced Cordless Technology) and Bluetooth speakers can have a similar effect.
If your household coverage is good, use the 5GHz range whenever possible to avoid interferences.
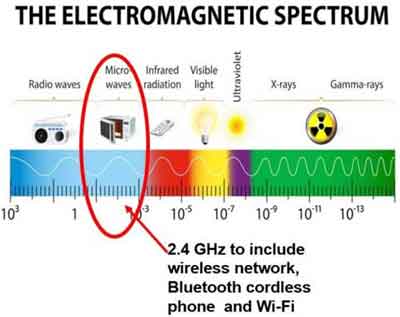 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingThe Electromagnetic Spectrum and Interferences
Source:- thegadgetsjudge.com
Optimizing Your Wireless Router's Capabilities
If you live in a flat complex or area with a lot of overlapping wireless networks, you can experience slowness in Internet performance, or even random disconnections.
This is likely because there are too many devices operating on the 2.4GHz frequency, and on the same frequency channel.
This is where you can optimize your routers capabilities by splitting your devices between the two bands, and changing the channels on each that are in use the least. This gives you the optimal setup for a consistent Wi-Fi connectivity experience and quality performance standards.
Wi-Fi bands or frequencies are governed by a set of protocols that adhere to a set of standards. This is what gives the different Wi-Fi settings their characteristics in terms of range and performance.
For example, the 802.11ac standard governs the 5GHz band, and the 802.11g standard governs the 2.4GHz band.
A quick way to determine your routers capabilities is to open a command prompt (Ctrl + R, followed by CMD), then enter the following command:-
- netsh wlan show drivers
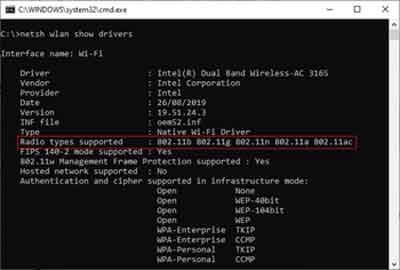 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingWireless Router Capabilities
As you can see, my home router supports both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. This gives me some options to think about.
For example, I can consider moving some of my home devices on to the 5GHz frequency, assuming they are capable of operating on that band.
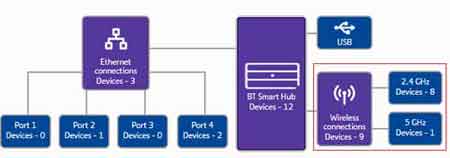 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingDevices Connected To Each Wireless Band
Now you have your devices split across the two bands, it is time to optimize the channel each band uses. The less channel overlap there is from friends and neighbours etc., networks, the less congestion there is, and therefore the better network performance you will experience.
The easiest way to do this is to let your router itself do the channel analysing and select the least used channel available at the time of analysis.
Alternatively, you can use utilities such as Wi-Fi Analyzer to manually determine which channels are best to use. A quick Google search will find this utility for you.
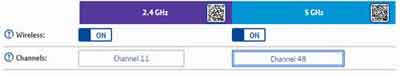 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingWireless Router Bands and Channels
Wi-Fi Performance Testing
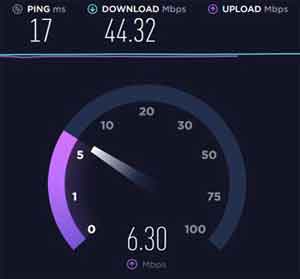
At this stage, your home Wi-Fi network setup should be optimized. If you are still experiencing issues, it is time to perform a broadband speed test.
This can be conducted either wirelessly, or by plugging your Laptop, for example, in to one of your router's Ethernet port, using the Ethernet cable supplied with your router.
If the download speed is much slower than usual, or what you are paying for, there is every chance the issue is with the ISP, and an outside chance of a hardware fault with your wireless router.
My suggestion is to contact your ISP. If they are not experiencing any issues, check with your landline provider and ask them to perform a health check on your line. You would be surprised how often the issue lies here. I've had it happen a couple of times recently.
Devices that do not belong to you can connect to unsecured wireless networks, and could be leaching all of your bandwidth.
Make sure your router is set up securely using WPA2, or WPA3, if available. If you do not have this security setup, then do so as soon as you get the chance.
Wi-Fi Protected Access v3 (WPA3) is more secure overall than WPA2, but common-sense precautions around online behaviour and general security should not be relaxed when using WPA3.
“Despite these issues with WPA3, our conclusion is still that WPA3 is a considerable improvement over WPA2 in terms of security and should remain in service for now.” Citation Maximilian Appel, Dr.-Ing. Stephan Guenther (2020) WPA 3 — Improvements over WPA 2 or broken again? In: Network Architectures and Services, November 2020.
More Extreme Steps If All Else Fails
If you have made it this far down the WiFi not working article, and are still experiencing issues, it is time to consider some of the more extreme actions to resolve your issue.
The first step is to complete a full reset of your Wi-Fi router. Most models have a Factory Reset button on the back.
Use a paper clip to press the recessed button (recessed to prevent accidental use). Often you need to keep the reset button pressed for up to 20 seconds. Once the router has booted, you will need to set up again from scratch.
Make sure you have the relevant information, such as SSID names and passwords, to save you having to reprogramme all of your devices.
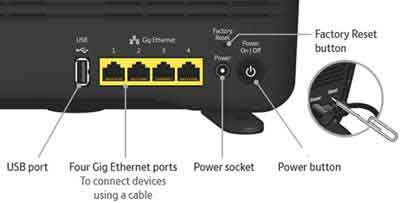 WiFi Not Working
WiFi Not WorkingResetting Your Wireless Router Example
Source:- bt.com
If this fails, the next steps are to think about manually updating the firmware on both your devices and your router. Your ISP usually takes care of your router updates, but often you can download the latest firmware package and install yourself.
There comes a time, however, when you need to consider replacing the router. This is especially the case if the router is several years old and has been heavily used by many active devices.
If you have access to a known working router, set this up in your home and connect one of your key devices.
WiFi Not Working | Final Thoughts
I hope the advice and guidance in the WiFi not working article have proven helpful, and even resolved your wireless issue(s) for you.
For additional support, have a look at the “Why is my WiFi not working?” article from Computer Hope, and the “Why you can't connect to Wi-Fi at home and what you can do about it" article from All Connect.
Finally, take a look at the short video below, which can offer further assistance in your quest to resolve your wireless connectivity issues. Good luck.